Data Analytics for Metal Cutting
Get deep insights to your machining processes and solve issues much faster
Machining Analytics Solutions
Higher output at equal quality, cost reduction and faster problem solving continue to challenge everyone in the metal cutting industry on a daily basis. Besides increasing transparency, automating processes and professional education advanced analytics allow to generate insight to solve problems faster than ever before. As c-Com we provide you with a software module that makes sense of your metal cutting data. Our software not only allows you to increase transparency by providing reports on demand, it also warns you proactively in case it predicts potential issues. Eventually this improves your productivity.
Data integration along the value stream

During the machining process of a workpiece many different data sources can be utilized to monitor progress and condition. Capturing and connecting these sources enables the creation of a digital twin of the part. c-Com Machining Analytics Software (MAS) puts the digital twin in context and thus allows for a better understanding of the process. Typical data sources MAS connects to are:
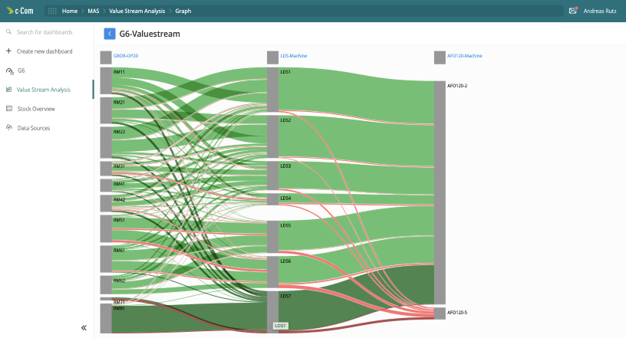
Value stream
If a problem occurs during the machining of a workpiece, troubleshooting can be very time-consuming, especially in series production. Many data sources need to be queried, combined and the results evaluated. The search for the origin of the issue is often like 'looking for a needle in a haystack'.
The MAS module monitors the data and detects anomalies on numerous data streams. Since all data is considered in the context of material cutting, the analysis provides indications of which production factor, for example, tool, machine, raw material is abnormal in the given case. MAS allows for a fast root cause analysis, digitally supporting the issue resoltuion phase to:
Active tool life monitoring
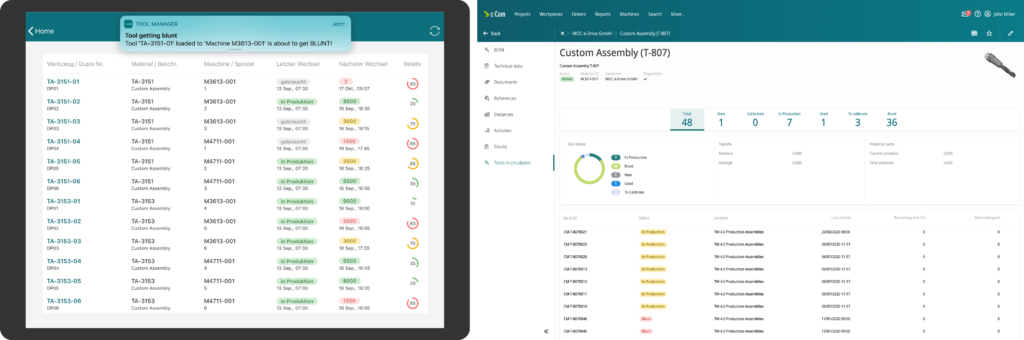
Which tool is in which machine/ spindle? How much tool life is left on a particular tool? When to change the tool next? These associated questions are answered by our partner-enabled tool tracking and monitoring solution. Most often, this solution relates to our tool management features as, to not only track the tool life of your assemblies, but also the tool life of serialized individual components. Please visit our Life Cycle Management section for further details on how to track individual cutting tools.
Tool wear analysis
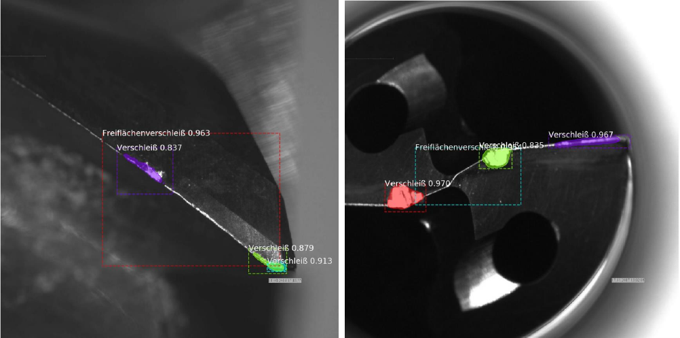
“Tool wear is a fingerprint of the process” is a popular phrase among tool manufacturers. How do i use the results of a tool wear detection solution?
Combining images and measurements of cutting tools our Machining Analytics Software/ tool wear analysis software identifies the cutting edges of a tool and evaluates its wear state. Together with information on an individually identifiable tool (for example, one with a QR/ data matrix code on it), the performance of the tool across refurbishment cycles is observed to spot issues in the process at an early stage. This indirect process monitoring additionally increases transparency on your tool stock and provides further benefits, such as:
Benefits of MAS
Optimize tool life
Stretch tool life with near real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustment of remaining tool capacities
Reduce scrap
Reduction of scrap parts and less time and measurement effort for parts produced in series by correlating measurement data with cutting data
Increase productivity
Increase productivity with optimized setup times (e.g. with early tool change notifications), increased quality (e.g. by forecasting trends even when measurements are still in tolerance) and improved overall equipment efficiency (OEE) enabled by notifications sent when anomalies are detected during machining
